As the demand for miniaturized, microelectronic, and high-power packages increases, substrates that can withstand high operating temperatures and provide excellent thermal performance become critical, so ceramic printed circuit board are becoming an important choice for PCB designers. With their thermal and mechanical advantages, they are gradually replacing traditional PCB as an effective solution to a wide range of electronic problems. In this article, ApplePCB will introduce you to the features of ceramic circuit boards, common materials, different processes and how to go about finding a reliable ceramic PCB manufacturer.
What is a Ceramic PCB?
Ceramic PCB are also known as green boards, where "green" does not refer to their color, but rather to their environmental properties. Compared to traditional FR-4, ceramic circuit board contain fewer toxic chemical and have a smaller carbon footprint. It is worth noting that the ceramics used in ceramic PCB are not the ordinary ceramics we use in our daily lives for flooring or pottery, but rather advanced ceramic materials that have undergone special industrial treatment and have a metallic component. These materials have excellent thermal conductivity, moisture, proofchemical resistance, and stability.
Besides, they also have significant advantages in environmental performance and service life. Commonly used in high-power electronics, automotive electronics, LED lighting, Radio Frequency (RF) and microwave electronics, medical devices, and other application.
Ceramic PCB, Heavy Copper PCB and Metal Core PCB
| Feature | Ceramic PCB | Heavy Copper PCB | Metal Core PCB |
| Base Material | Al2O3, AlN, BeO, SiC, BN | FR-4 (with thick copper) | Aluminum, Copper, Iron |
| Thermal Conductivity | Highest | High | High |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Good (depends on copper thickness and insulation design) | Good |
| Current Carrying Capacity | Relatively low | Highest | Moderate |
| Hardness | High hardness, brittle | High hardness, corrosion-resistant | High hardness |
| Weight | Relatively low | Heaviest | Light (Aluminum) or heavier (Copper) |
| Cost | High (expensive) | Moderate | Low (Aluminum) or heavier (Copper) |
● ApplePCB's Advice:
Overall, if your application demand high current carrying capacity, thick copper PCB is a good choice. For efficient heat dissipation on a lower budget, aluminum PCB is recommended. However, if you have a larger budget and need superior thermal conductivity, excellent electrical insulation, high-frequency performance, and high-temperature stability, ceramic PCB is the best option.
Common Ceramic Materials
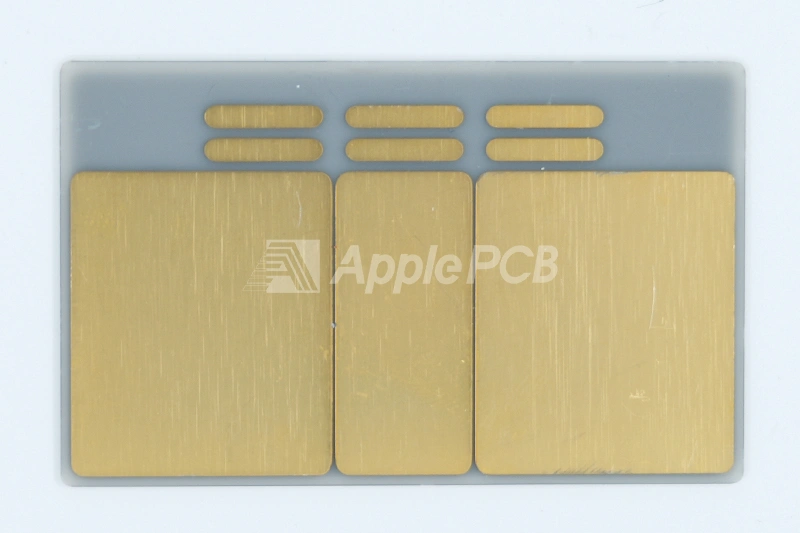

Currently ApplePCB can provide ceramic PCB substrate materials: Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3), Aluminum Nitride (AlN), Beryllium Oxide (BeO), Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Boron Nitride (BN). The most common of these are Al2O3 PCB and aluminum nitride PCB. In the table below we compare the two materials in terms of their physical, electrical, mechanical and thermal properties.
| PROPERTY | ITEMS | Unit | Al2O3 96% | AlN |
| Physical | Color | - | White | Grey |
| Water absorption | % | 0 | 0 | |
| Reflectivity | % | 94(1mm) | 30(0.5mm) | |
| Electrical | Dielectric Constant (1MHz) | - | 9~10 | 8~10 |
| Dielectric Loss | *10^-4 | 3 | 3 | |
| Dielectric Strength | MV/m or KV/mm | >15 | >17 | |
| Insulation/Volume resistance | Ω·cm | >10^14 | >10^14 | |
| Mechanical | Density after Sintering (Bulk density) | g/cm3 | >3.7 | 3.26 |
| Flexural Strength(3 point) | Mpa | >400 | ~380 | |
| Surface Roughness | μm | 0.2~0.75 | 0.3~0.6 | |
| Camber | Length% | ≤2 | ≤2 | |
| Thermal | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | ppm/°C | 6.5-7.5 | 2~3 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion RT~500°C | ppm/°C | 6.5-8.0 | 2.5~3.5 | |
| Thermal Conductivity(25°C) | W/m·K | 24 | 170 |
● ApplePCB's Advice:
If your device needs high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, aluminum nitride is the best option if your budget permit. However, if your application require slightly lower thermal performance and emphasizes cost control, aluminum oxide is a viable alternative. This is because aluminum oxide has been extensively studied and its manufacturing technology is highly developed.
Comparison of Ceramic and FR-4 Materials
Ceramic and FR-4 are both used materials, each with its strengths. By examining the distinctions, between these two materials ApplePCB aims to assist you in making informed decisions when designing and producing PCBs.
1. Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of ceramic materials is much higher than FR-4, ceramic materials with the lower thermal conductivity of alumina are 30 times the thermal conductivity of FR-4, and aluminum nitride is more than 170 times the FR-4. So for common heat dissipation needs, we can choose to use FR-4 PCB and effective heat dissipation design. For high-power applications, FR-4 may have component failures due to heat dissipation problems, resulting in lower reliability, so ceramic material is a better choice.
2. Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
FR-4 has a CET of about 12-18pm/c, while the average for chips soldered to PCB is about 6pm/c. There is a significant difference between them. The CET value of FR-4 is higher than chip, so when they are heated at the same time, FR-4 expand more drastically than the chip, which leads to the problem of solder joints falling off from the chip. The CET value of ceramic material is within the range of 2-7ppm/°C, which is very close to, and may even be lower than chip, and therefore can maintain product reliability in LED, which are subject to drastic temperature changes.
3. Dielectric Constant and Loss Angle Tangent
In high-frequency application, dielectric constant and loss angle tangent are critical factors that designers must consider to ensure signal distortion is minimized and signal integrity is optimized. Ceramic materials typically have dielectric constants in the range of 5 to 200 and loss angle tangents in the range of 0.001 to 0.05. In contrast, FR4 materials typically have dielectric constants in the 4 to 5 range and loss angle tangents in the 0.01 to 0.02 range. Clearly, ceramics outperform FR-4 in both respects. Therefore, in high-speed digital system and RF circuit, ceramic boards provide better signal quality and reduced signal attenuation.
4. Processing Difficulty
Processing Ceramic PCBs poses challenges compared to FR-4. This is because ceramics are brittle materials increasing the risk of breakage during manufacturing. As a result manufacturers need to exercise caution when handling them. In addition, the production of ceramic printed circuit board usually involve more specialized manufacturing technique such as laser cutting, thick or thin film deposition, and co-firing process. In contrast, FR-4, as a widely used standard PCB material, is well established and manufacturers have gained extensive experience in manufacturing technique such as etching, drilling and soldering.
● Why Do Ceramic Boards Break Easily?
Ceramic substrates differ from FR 4 as they are crafted from inorganic materials. These materials possess specific chemical bonds and their crystal structures lack slip systems. As a result when ceramic materials undergo stress they struggle to release the pressure through deformation. Moreover the wrong use of materials or inadequate sintering can lead to a fragile end product. To combat this issue ApplePCB utilizes high purity materials and precise laser equipment in the production of ceramic circuit boards to prevent cracks and defects caused by processing stress. When installing and using ceramic plates, our professional staff will hold them gently throughout to prevent violent impacts.
5. Cost
Overall the material cost of FR-4 is lower because they are easily available as a standard choice for PCB. And due to high market demand and standardized production process, the cost of FR-4 PCB will be further reduced. In contrast, ceramic PCB have higher material cost and more stringent manufacturing process requirement, which results in a larger upfront investment, but ceramic material has a long service life and offer better thermal conductivity. Therefore, in the long run, this initial high investment can bring significant returns.
Various Categories of Ceramic PCB
Based on manufacturing methods ceramic PCBs can be classified into the following types:
High Temperature co-fired Ceramic PCB (HTCC PCB)
This is the most traditional manufacturing method and no glass is added in this method. Aluminum oxide is mixed with binders, plasticizers, lubricants, and solvents through roll forming and curtain coating techniques, and then circuit traced on high melting point metals such as tungsten and molybdenum. Next, these ceramic materials are baked at high temperatures for 32 to 48 hours at temperatures ranging from 1,600°C to 1,700°C. ApplePCB accurately controls the hydrogen or other reducing gas environment during the baking process, effectively preventing oxidation of the refractory metals.
Because high-temperature co-fired ceramic PCBs face shrinkage tolerance and warpage issues in larger boards, as well as higher tracing of refractory metals, ceramic circuit board manufactured through this high-temperature co-firing process are more suitable for small boards, derivative boards, or carrier circuits. ApplePCB's high-temperature co-fired ceramic PCBs are used in a wide variety of high-performance electronics, including high-power LEDs, power amplifiers, inductors, sensors, and energy storage capacitors.
Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic PCB (LTCC PCB)
This process is accomplished by heating in a gaseous oven at 900°C, allowing us to use highly conductive gold paste for circuit tracing. Besides the temperature, the main difference between LTCC PCB and HTCC PCB is that LTCC PCB incorporate about 30%-50% glass material mixed with ceramic material to improve the thermal properties of the material. As a result, LTCC PCB have excellent thermal and electrical properties. ApplePCB's low-temperature co-fired ceramic PCB is widely used in microwave module, antenna module, pressure sensor, gas sensor, accelerometer, microwave filter, power divider, and other device.
Thick Film Ceramic PCB
Thick film ceramic PCB has excellent thermal shock resistance and thermal stability. In addition, it has a relatively simple manufacturing process, high manufacturing efficiency, and low cost. Through multiple silkscreen layers, the thickness of the metal layer can be effectively increased. the thickness of the metal line layer of ApplePCB's thick film ceramic PCB range from 10μm to 20μm. its baking temperature is generally 850°C~900°C. However, to improve the bonding strength between the metal layer and the ceramic substrate, the manufacturer will add a small amount of glass material to the metal paste, thus affecting the electrical and thermal conductivity of the metal layer.
Thin Film Ceramic PCB
Thin-film ceramic PCB film thickness is generally less than 1μm, and the operating temperature is generally less than 300°C, which can prevent high temperatures for the destruction of metal materials. In addition, unlike the thick film Silkscreen process, the manufacturing process of thin-film ceramic PCB is more complex, ApplePCB has mastered the magnetron sputtering, vacuum evaporation electrochemical deposition, and other advanced thin-film process, which can ensure the reliability of the metal layer. Compared with thick-film ceramic PCBs, thin-film ceramic PCBs have better thermal conductivity and also support higher-density wiring (line width line spacing less than 10μm). It is commonly used in lasers, LEDs, and other devices with high power, small size, high heat dissipation requirements.
Laser Activated Metallization PCB(LAM PCB)
Laser Activated Metallization PCB, also known as LAM PCB involves the process of ionizing ceramics and metals with a high-energy laser to create a bond. This method offers benefits such, as a smoother surface texture, increased material strength, and improved thermal conductivity. LAM PCB technology finds applications, in high-power LED lighting systems, electric vehicles, and power modules.
Direct Plate Copper PCB (DPC PCB)
Direct Plate Copper PCB are made by physical vapor deposition, vacuum, and sputtering to bond copper to a ceramic substrate at high temperature and high pressure. This process provides high strength, high thermal conductivity, and excellent electrical performance, making it ideal for LED light, UV LED, COB LED, and other products. Noteworthy, DPC PCB is available in copper thickness ranging from 2μm to 105μm, so if you need a thicker copper thickness, you should consider DBC PCB which is in the following.
Direct Bond Copper PCB (DBC PCB)
If you need ceramic PCB larger than 150 μm, then you need to use the DBC process. ApplePCB can manufacture DBC PCB up to 300 μm. A Cu-O eutectic liquid is formed by introducing an appropriate amount of oxygen between the copper and the ceramic before (or during) deposition. The ceramic substrate and the Cu-O eutectic are then placed at an elevated temperature of 1065°C to 1083°C to chemically react to produce CuAlO2 or CuAl2O4, which penetrate through the copper foil to achieve a strong bond between the copper foil and the ceramic substrate. DBC PCB produced by ApplePCB has been widely used in power supply module, power electronic device, and electric vehicle controller.
How to Find a Reliable Ceramic PCB Manufacturer?

When selecting a manufacturer, for ceramic PCBs keep in mind these aspects that can guide you in finding a trustworthy partner:
1. Manufacturing Experience and Equipment
According to your product program, you should choose a ceramic PCB manufacturer with relevant rich experience, ApplePCB has 15 years of rich experience in ceramic PCB manufacturing, we have a professional team of engineers, all of whom have more than 10 years of experience in ceramic PCB. In addition, ApplePCB has specialized ceramic PCB manufacturing plants in Shenzhen and Chongqing, covering a total area of 95,000 square feet, with advanced production equipment such as fully automatic mixing and stirring systems, laser drilling and cutting machines, and high-temperature sintering furnaces.
2. Material and Process Capabilities
Ensure that the manufacturer can provide a wide range of material choices and have the fabrication process to match your ceramic PCB. ApplePCB can provide five types of ceramic materials: Al2O3, AlN, BeO, SiC, and BN to meet different needs. Our specific capabilities are as follow:
| Specifications | Capabilities |
| Layers | 1-8 Layer |
| Solder Mask | Black,Green, Red, Yellow, White, Blue |
| Thermal Conductivity | 24-170W/K.M |
| Thicker Copper | 1/3OZ-12OZ |
| Finished Board Thickness | 0.4MM-5MM |
| Panel Sizes | Master Panel:115 x 115mm |
| Usable Areas:105 x 105mm | |
| Special Panels:170 x 250mm | |
| Usable Areas:160 x 240mm | |
| Aspect Ratio | 8/1 |
| Minimum Line Width and Spacing | 0.01mm |
| Copper Thickness | 2μm to 105μm (DPC) |
| Trace width/space | 150μm to 300μm (DBC) |
| 5-10μm: 0.05mm/0.05mm | |
| HOZ: 0.075mm/0.075mm | |
| 1OZ: 0.1mm/0.1mm | |
| 2OZ: 0.127mm/0.127mm | |
| 3OZ: 0.3mm/0.3mm | |
| 6OZ: 0.5mm/0.5mm | |
| 9OZ: 0.6mm/0.6mm | |
| Finished Surface | Immersion Silver, Immersion Gold, Nickel Palladium Gold |
| (Support for selective applications) | |
| Technology | Thick/Thin film, DBC, DPC(3D), LAM, LTCC, HTCC |
| Laser drill | ≥60μm |
| Rules | DFM, DFA |
3. Packaging and Transportation
Given the fragility of ceramic board, ApplePCB uses specially designed high-protection packaging boxes for ceramic PCB. Each board is wrapped in pearl cotton or foam for extra protection. The boxes have internal support plates and V-shaped grooves to prevent collisions. Additionally anti-static blue film is placed between each board to provide further protection. The boxes are kept dry and ventilated during transport to avoid moisture and direct sunlight. These measures ensure that the ceramic boards remain intact during shipping.
4. Quality Certification
Choosing a manufacturer with relevant quality certifications is crucial to ensure the quality of ceramic PCB, especially in the medical and automotive industries. ApplePCB produce all ceramic PCB in compliance with IPC and ROHS. Besides we have been awarded several quality certifications. These ensure that our products are above international standard and meet various stringent quality requirements.
● IATF 16949:2016
● ISO 9001:2015
● ISO14001:2015
● ISO13485:2016
● UL
5. Successful Product Cases
By looking at ceramic PCB suppliers' success cases, you can gain insight into the practical applications and performance of the products they produce in different field. ApplePCB's ceramic PCB is widely used in several demanding field such as ECU, antennae, RF filter, MRI, CT scanner, and high-power LED lighting system. We demonstrate our adaptability and technical advantages in different application scenarios.
6. Customer Service
For ceramic PCB which are difficult to manufacture, some complexities may arise during the ceramic PCB manufacturing process, which requires timely and quality customer service to ensure the smooth and efficient progress of the project. From design consultation to after-sales service, ApplePCB provides 24/7 technical support, our customer service team is committed to responding to customer needs within 1 hour, overcoming geographical constraints and time differences to ensure that customer around the world can get timely support. ApplePCB's customer service satisfaction rate of 99%, we are committed to providing each customer with a quality service experience.
